Gaze Based Multi Agent Control

A gaze based system for intuitive and user friendly control of multi-agent systems. Completed for the final project of ME 396P - Applications of Programming for Engineers.
Published on December 05, 2024 by John Lyle
Python Object Oriented Programming Data Filtering Algorithms
Summary
Problem Statement: Create a demo illustrating usage of a gaze based agent selection system for control of multi agent systems.
Project Details: This project was selected by our team due to possible expansions into future research applications as well as an interesting overall goal. We contemplated a few different demonstrations but ultimately decided upon a turtle environment where a webcam would determine which turtle was being looked at by the user. This would allow the user to control the selected turtle with the arrow keys of a keyboard. The project was split into three main parts which were gaze location detection, agent selection, and the turtle environment. I worked on the agent selection and overall integration portion of the project.
Environment and Usage Overview
Calibration: Each time the program is used a quick calibration sequence is used. This calibration sequence is then saved for future use if the same display and camera are detected. Below is a GIF of the calibration sequence. This is used to obtain accurate readings of where the user is looking to determine which agent they want to control.

Demonstration: Once the calibration sequence is finished the turtle environment is opened. The user simply looks at which turtle they want to control and uses the arrow keys to do so. There are also a few other controls detailed in the top left that can be used to change speed settings.

Agent Selection Methodology
My primary contribution to this project was the method of determining which agent was being viewed. I wanted to create something that was robust yet quick and easy to use. The final product ended up being a combination of the below methods.
Position Based: The simplest method of selection is based on which agent the gaze position is closest to. When other methods come up inconclusive the program defaults to this method. This method is incredibly reliable yet when the turtles are far apart it takes a while to recognize that the user has switched their focus.
Velocity Based: This is the primary method of selection for this program. I implemented a Kalman filter so that the velocity of the user’s gaze can be approximated from the time-series position data. This logic then uses the difference between the velocity vector and the vector from the gaze location to the turtle location to determine where the user is on the way to looking. Without any constraints, this method is not very robust. I constrained the logic even further to require a minimum threshold velocity to be surpassed and for the angle between the vectors to be within a certain range. This ensures that the correct agent is selected whenever velocity-based selection is used. If these criteria are not met, then the position-based selection is used as a fallback.
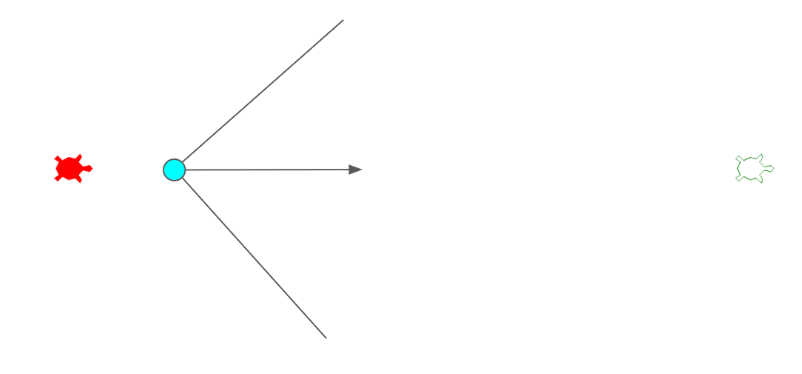
Classifier Model: (IN PROGRESS) The implementation of a classifier will be explored if this project is continued and used in expanded applications. This would likely use some sort of random forest classifier. This would allow us to take ground truth data of what agent the user is attempting to control from collected samples and figure out what signals indicate a user has switched their focus.
Additional Information
Any future work related to this project will be linked here as well.